- <Z/A> has not been recalculated for revised atomic masses. In no application here does it matter, and in any case the changes should not affect a number given to only five places.
-
Rossi's definition of critical energy is used: It is the energy
at which the (negative) electron ionization per radiation length
is equal to the electron energy. This is said to give a Moliere radius
value more in agreement with experiment than the ionization loss rate =
radiative loss rate algorithm.
In contrast, the muon critical energy given in the table is the energy at which ionization and radiative loss rates are equal. - For most compounds and mixtures, effective ionization energies and density effect parameters are from early papers by Sternheimer, Selter and Berger, notably S. M Seltzer & M. J. Berger, Int. J. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 33, 1189 (1953). For some which are not in the original tables, the ionization energies are either found in the literature (NaCl) or by Bragg addition with the famous 13% correction. The density effect parameters are then calculated using the algorithm given by Sternheimer and Peierls (Phys. Rev. B 3, 3681 (1971)).
- The data file used to generate these tables can include properties such as boiling and melting points in a fairly open-ended way. For examples see Al2O3 and methane. Inserting the numbers by hand is fairly laborious. More will be added when volunteers appear.
- Index of refraction is evaluated at the sodium D line (blend of 589.0 nm and 589.6 nm; weighted average 589.2 nm).
- Most polymers do not have a well-defined specific gravity or index of refraction. The values given should be regarded as typical, not absolute.
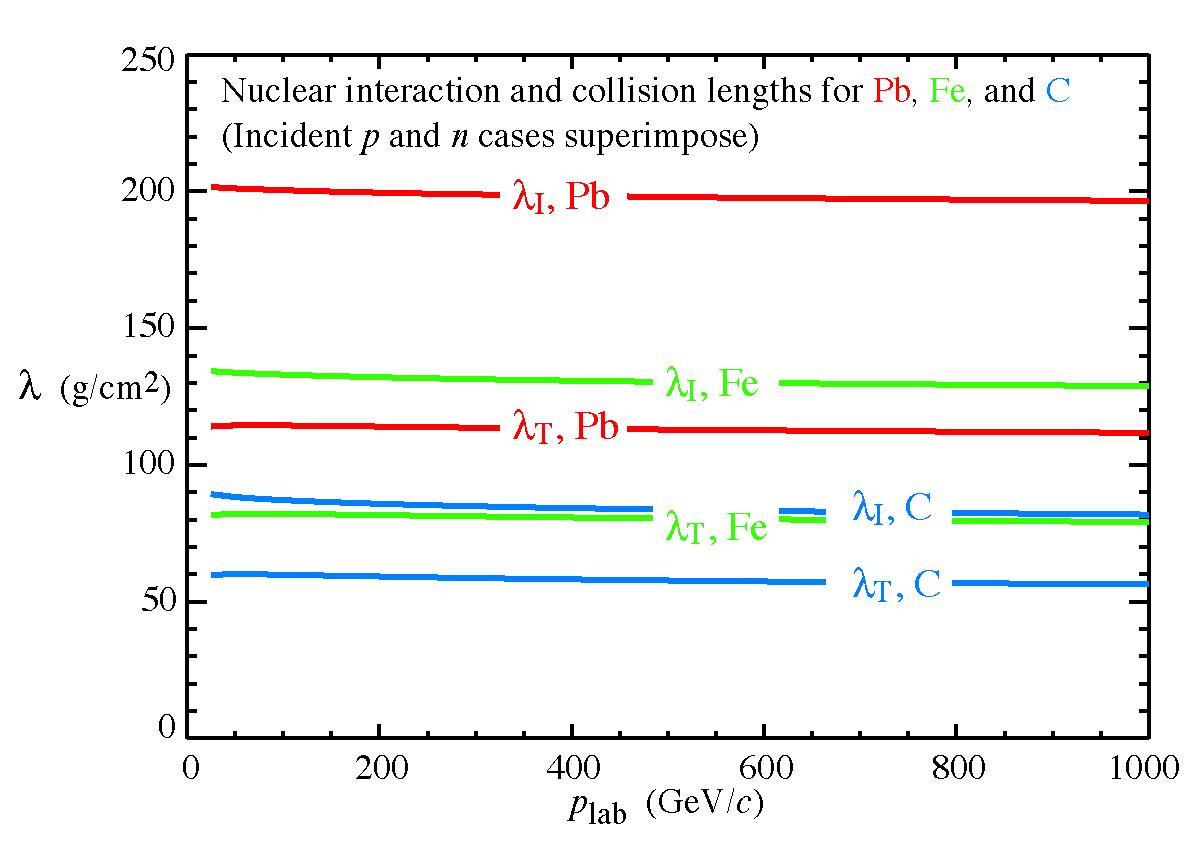
- For compounds and mixtures, Bragg addition (mass fraction weighted sum) is used to calculate muon radiative loss rate and the reciprocals of radiation length, nuclear collison length, and nuclear interaction length.
Revised 2014 August 12 by DEG